If you’re concerned about the development of kidney stones, you’re not alone. Many people are also prone to developing them, due to certain conditions and diets. However, knowing what causes kidney stones can help you prevent or reduce your risk. Here are some common causes and ways to avoid them. Know your genetics to reduce your risk. Some of the most common causes of kidney stones are lifestyle, diet, and genetics. Know what your family members ate, and what your family has done for kidney stones.
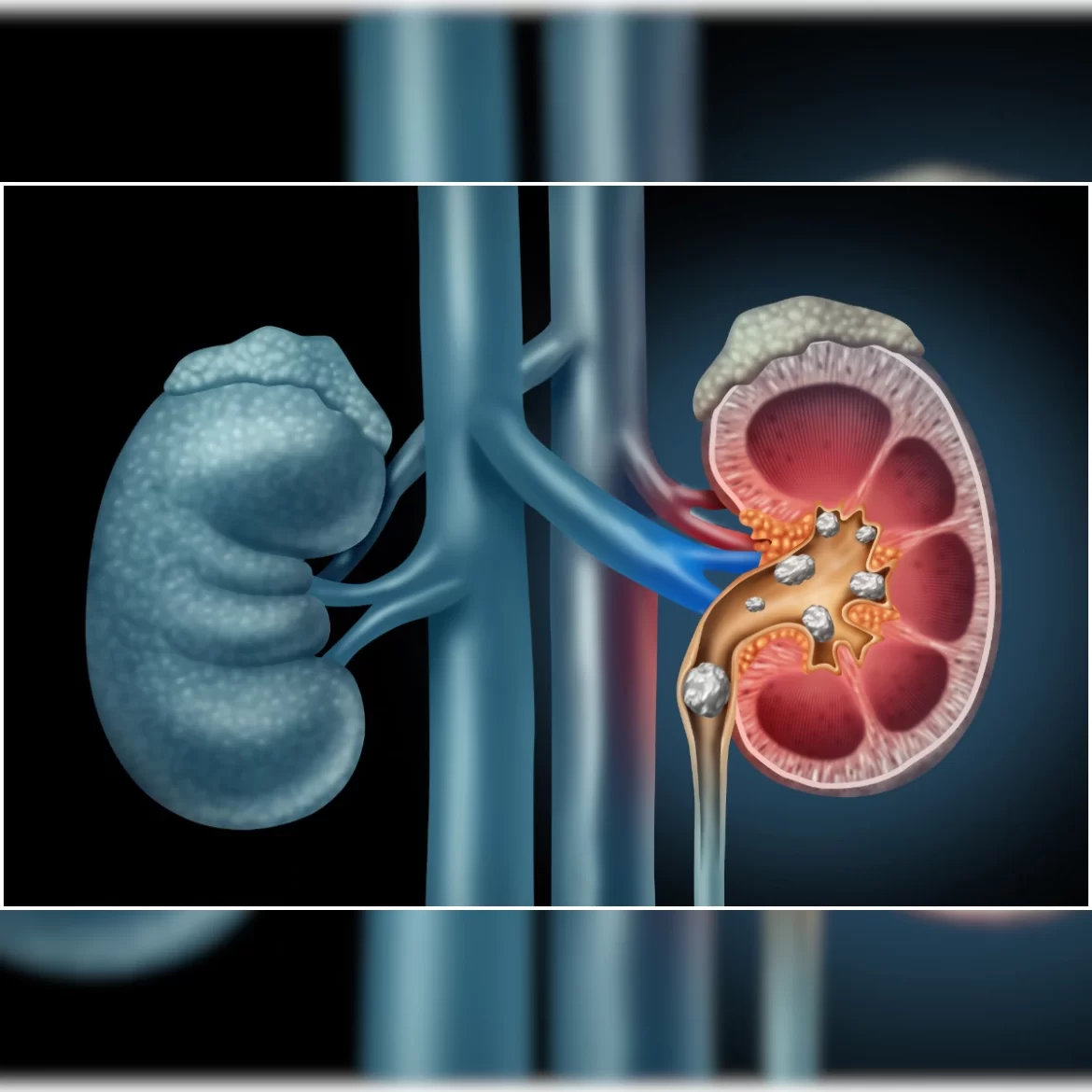
Your urine contains various wastes, including calcium, phosphate, and oxalate. When too much of any one of these elements accumulates in the kidney, they form a crystal, which attracts other elements and eventually grows. Unless these solids are removed with your urine, they will continue to grow. Other chemicals found in urine help prevent the formation of stones. But some of these chemicals can cause kidney stones. These chemicals include calcium, oxalate, urate, cystine, xanthine, and phosphate.
While the calcium content of urine is generally normal, the presence of excess calcium in the urine can lead to kidney stones. Some people’s urine may be more concentrated than normal, so it may be a sign of an abnormal kidney. Some stones may also occur as the result of cysts or scarring on the kidney. Some people are more susceptible to developing kidney stones due to their genetics or lifestyle, or even because a family member has them.
If your child has a high mineral level in urine, or dehydration, they can develop kidney stones. Both of these factors can lead to the development of these stones, and the condition may even be caused by inborn metabolic problems. In rare cases, kidney stones can be passed from one family member to another. However, this type of kidney stone is usually hereditary, and is passed down through a parent. It can also be caused by a traumatic injury to the kidney.
In addition to the above mentioned causes, you should drink 8 to 10 glasses of water each day. Also, avoid drinking foods high in oxalate, which is a natural component of many foods. A high oxalate level can also lead to stones. For example, you should limit your intake of processed foods, such as processed meat and dairy products. The same applies for eating too much food high in sodium. If you do consume foods high in sodium, your risk of kidney stones increases.
Diet is also another major cause. Too much salt can lead to kidney stones, so limiting the amount of salt in your diet can reduce the risk. Too much sodium and sugar raise the calcium in your urine, which increases the risk of kidney stones. You should also limit your intake of oxalate-rich foods such as beans, nuts, wheat bran, sweet potatoes, and dark green vegetables like spinach. Certain medical conditions can increase your risk of developing kidney stones, including high blood pressure and diabetes.